唇瘡 痱滋 | Aphthous Ulcer
什麼是阿弗他潰瘍(唇/口瘡)?
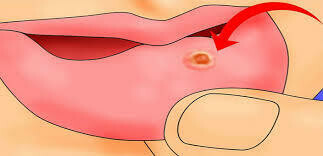
阿弗他口腔潰瘍(aphthae)是一種常見的潰瘍,形成於粘膜,通常長在口腔內。唇瘡的其他名稱包括阿弗他口炎和潰瘍。
唇瘡通常是圓形的形狀長於嘴內,如嘴唇內部,臉頰內或舌底。他們是良性的,非傳染性的,可以發生單一的潰瘍或集羣。
在大多數情况下,唇瘡是會復發性的,這種情況被稱為復發性阿弗他口炎(RAS),每次發作通常持續7到10天。
這種情況的原因尚不清楚,也沒有治癒的方法,但可以選擇治療潰瘍可能引起的疼痛。
唇瘡是最常見的口腔潰瘍類型,但他們不是唯一的一種。
主要有三種類型:
小口瘡
這些是最常見的品種。它們體積小,直徑通常小於5毫米,可形成單一潰瘍或叢生潰瘍。它們通常不會引起太多疼痛。
大阿弗他潰瘍
這些是不太常見的,通常是5毫米或更大,形成單一或成對。他們可能會很痛苦,尤其是在吃或喝的時候,而且會持續兩周到幾個月。
皰疹樣潰瘍
當多個病灶融合在一起形成不規則形狀的大潰瘍時,就會發生這種情況。皰疹樣潰瘍之所以被稱為皰疹,是因為它們在外觀上與皰疹相似,然而,皰疹樣潰瘍並不是由單純皰疹病毒引起的。
高濃参碱蜂膠液 (食用加外塗)
在這項隨機、雙盲、安慰劑對照研究中,患者被分配每天服用500毫克蜂膠或安慰劑膠囊。受試者報告基線潰瘍頻率,並每兩周聯系一次以記錄復發情况。對數據進行分析,以確定受試者的爆發頻率是否下降了50%。
資料表明蜂膠組的暴發在統計學上顯著减少(Fisher精確檢驗,單側,p=0.04)。蜂膠組的患者也自我報告其生活質量顯著改善(p=0.03)。
這項研究表明蜂膠能有效地减少RAS患者的復發次數,提高患者的生活質量。
唇/口瘡 - 多學科研證復康方案
- 藥物及其他醫療方案, 請遵醫從醫生建議
- 飲食營養請依營養師指引
- 運動及或心理輔導, 請參考各專家建議
- 為免錯誤診斷及漏診, 請上傳最近一個月醫院的專業診斷報告。
可能適合的補充劑支援:
標準組合:
試用時期: 1星期
如你有任何疾病, 請遵照閣下醫生的完整醫療方案; 而是否使用多學科復康方案前, 你必須咨詢主診醫生的意見, 如果閣下的主診醫生不建議您加入補充劑調理組合, 請你不要使用。如果你需要尋求其他醫生作第二咨詢, 閣下可聯絡我們線上<無邊界醫生>或你自己城市內的其他專業醫生的再診斷。
__
What Are Aphthous Ulcers?
Aphthous mouth ulcers (aphthae) are a common variety of ulcer that form on the mucous membranes, typically in the oral cavity (mouth). Other names for aphthous ulcers include aphthous stomatitis and canker sores.
Aphthous ulcers are generally round in shape and form in the soft areas of the mouth such as the inside of the lips, the cheeks or the underside of the tongue. They are benign, non-contagious and can occur as single ulcers or in clusters.
In most instances, aphthous ulcers are recurrent – a condition known as recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS) – with each episode normally lasting for between 7 and 10 days.
The cause of the condition is unclear, and there is no cure, but treatment options are available to treat the pain the ulcers can cause.
Aphthous ulcers are the most common type of mouth ulcer, but they are not the only kind of mouth ulcers.
There are three main types:
Minor Aphthous Ulcers
These are the most common variety. They are small in size – usually less than 5 mm in diameter – and can form as a single ulcer or in a cluster. They typically do not cause much pain.
Major Aphthous Ulcers
These are less common, are generally 5 mm or larger and form singularly or in a pair. They can be painful, especially when eating or drinking, and last anywhere between two weeks and a number of months.
Herpetiform Ulcers
These can occur when multiple pinpoint lesions fuse together and form large, irregularly shaped ulcers. Herpetiform ulcers are so called because of their similarity in appearance to herpes, however, herpetiform ulceration is not caused by the herpes simplex virus.
High Concentration Matrine Propolis (Oral and Topical)
The purpose of this pilot study was to evaluate the potential of a product to reduce the number of outbreaks of RAS ulcers.
Propolis is a bee product used in some cultures as treatment for mouth ulcers. In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, patients were assigned to take 500 mg of propolis or a placebo capsule daily. Subjects reported a baseline ulcer frequency and were contacted biweekly to record recurrences. Data were analyzed to determine if subjects had a decrease of 50% in outbreak frequency.
The data indicated a statistically significant reduction of outbreaks in the propolis group (Fisher's exact test, one sided, p = 0.04). Patients in the propolis group also self-reported a significant improvement in their quality of life (p = 0.03).
This study has shown propolis to be effective in decreasing the number of recurrences and improve the quality of life in patients who suffer from RAS.
Multidisciplinary rehabilitation program for Aphthous Ulcers
- Please follow the doctor's advice for drugs and other medical plans
- Please follow nutritionist's guidance
- For sports or psychological counseling, please refer to the experts' suggestions
- In order to avoid misdiagnosis, please upload the latest health report from hospital (preferably dated within a month)
Suggested supplements:
Standard combination:
Trial period: 1 week
If you have a medical condition, please follow your doctor's medical treatment plan. Do consult your medical doctor before using the Multidisciplinary Rehabilitation Program (MRP). Please do not proceed if your medical doctor does not recommend the use of our MRP. If you'd like to seek a second opinion from other doctors, you may contact our online "Doctors Without Border", or other professional doctors at your convenience.
__
參考研究 / Ref:
- Nachum Samet 1 , Caroline Laurent, Srinivas M Susarla, Naama Samet-Rubinsteen The effect of bee propolis on recurrent aphthous stomatitis: a pilot study Clin Oral Investig . 2007 Jun;11(2):143-7. doi: 10.1007/s00784-006-0090-z. Epub 2007 Feb 7. PMID: 17285269 . DOI: 10.1007/s00784-006-0090-z
__
本品等並非根據《藥劑業及毒藥條例》或《中醫藥條例》注册。任何對其提出的宣稱均不受此類登記評估的約束。本產品不用於診斷、治療或預防任何疾病。
Products are not registered under the Pharmacy and Poisons Ordinance or the Chinese Medicine Ordinance. Any claim made for it has not been subject to evaluation for such registration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat or prevent any disease.